Phytochemical, Toxicological, and Anti-Hyperglycemic Evaluation of Pennisetum purpureum in Sprague-Dawley Rats
Abstract
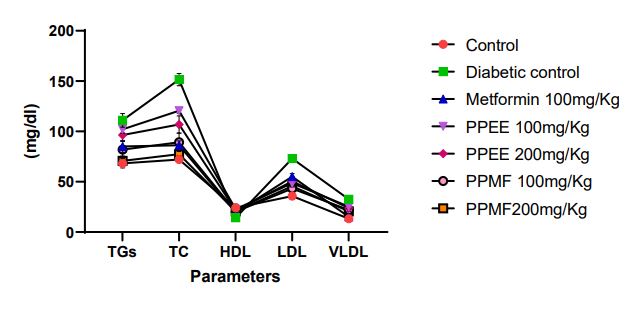
Many herbal extracts have been used for preventing and managing diabetes. In recent times it was documented that the herbal extracts in traditional Indian medicine are clinically effective in treating sugar imbalances associated with diabetes mellitus. Although it was considered that several bioactivities and phytochemicals have been attributed and it confirmed in terms of their toxicological profile and anti-diabetic activity. Herbal formulation and extract of the plant part of elephant grass plays an important role for the treatment of various diseases and disorders such as inflammation, pain, ulcer, cancer, bacterial infections, and fungal infections. Ethanolic extract of Pennisetum purpureum which was prepared by using 50%v/v and their fractions were prepared by using liquid-liquid extraction technique. There was quantitative estimation of gallic acid analyzed by HPTLC technique. The extract has been found safe at high dose through oral acute toxicity study. Antihyperglycemic activity was performed on Sprague Dawley rats by inducing the diabetes through Streptozotocin. Gallic acid was quantitatively estimated in methanolic fraction of extract and was found to be 0.13%w/w. Extract showed positive response in the treatment of diabetes which was confirmed after performing histopathology of liver and pancreas. Finally in this study, it was found that P. purpureum showed no toxicity and ameliorative changes in the blood glucose level, antioxidant level and biochemical parameters viz. triglycerides, total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein, low density lipoprotein and very low density lipoprotein.